Biosystematics and Phylogenetics: Understanding the Relationships of Life on Earth
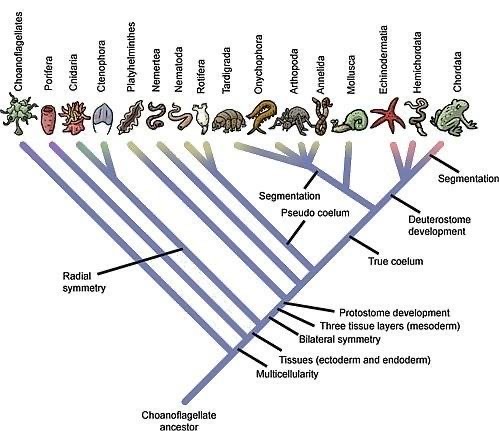
Phylogenetic tree of the animal kingdom (Photo Credit : Aiasha Siddika Arshi)
Biosystematics and phylogenetics are branches of biology that are interconnected in the study of the diversity of living organisms and the relationships between species. Both are essential for understanding the evolution and history of life on Earth. Biosystematics groups organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary relationships, while phylogenetics builds a “tree of life” to map out species evolution from common ancestors.
Biosystematics studies the classification and grouping of organisms. Through biosystematics, scientists can identify, describe, and group species based on certain characteristics to understand the relationship patterns between species and groups of organisms. Taxonomy and classification form the foundation of biosystematics, where living organisms are grouped into taxa based on morphological, genetic, and other similarities.
Phylogenetics focuses on the evolutionary relationships between organisms, using genetic, morphological, and fossil data to build phylogenetic trees that depict evolutionary history and lineage paths from a common ancestor. These phylogenetic trees reveal species diversification and adaptation patterns over time.
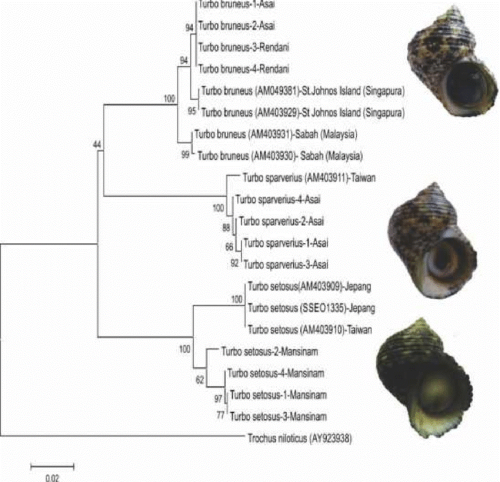

Phylogenetic Tree of Turbo Species in Manokwari Waters, West Papua (Photo Credit : Dandi Saleky)
Examples of Biosystematics and Phylogenetics
In bird classification, scientists initially relied on morphological features like beak shape and feather color. However, DNA analysis has shown that birds that look similar are not necessarily closely related. For example, the kiwi bird is actually closer to small birds rather than large flightless birds like the ostrich. Additionally, in phylogenetic studies of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, genetic data revealed its closeness to bat viruses and helped trace the spread of variants from one region to another.
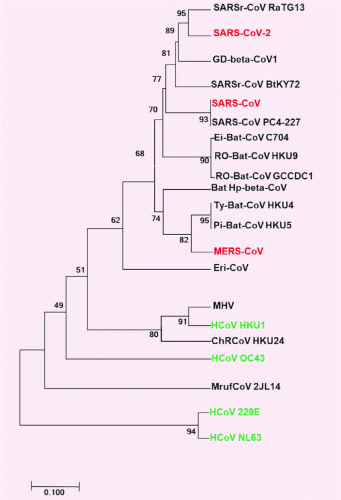
Phylogenetic tree of representative species of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV (Photo Credit : Salma Mukhtar)
Structure of a Phylogenetic Tree
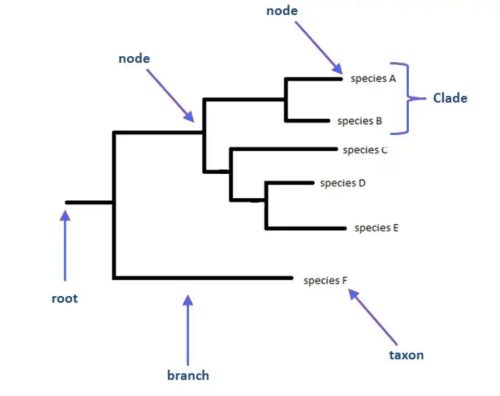
Parts of phylogenetic tree (Photo Credit : BNO Team)
- Root: The starting point showing the common ancestor.
- Branch: Indicates the evolutionary path of an organism or group.
- Node: A branching point indicating species or group divergence.
- Clade: A group of organisms consisting of a common ancestor and all its descendants.
- Leaf/Tip: Represents the organisms or species that exist today.
Types of Phylogenetic Tree
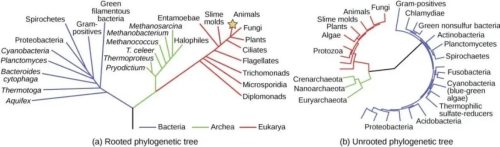
Rooted and unrooted tree (Photo Credit : BNO Team)
- Rooted Tree: Shows evolutionary relationships with a time order from ancestor to descendants.
- Unrooted Tree: Depicts relationships between species without evolutionary order.
Steps in Creating a Phylogenetic Tree
- Data Collection: Data can include DNA sequences, morphology, or other data. Genetic data is more commonly used because of its accuracy.
- Choosing an Analysis Method: Commonly used methods include Maximum Likelihood, Bayesian Inference, and Parsimony, selected based on data complexity.
- Tree Reconstruction: Data analysis is done using software like MEGA or BEAST to produce a phylogenetic tree.
In the COVID-19 pandemic, phylogenetic trees were used to trace the origin of SARS-CoV-2 and identify emerging variants. By comparing genetic sequences from samples taken from various countries, scientists could observe how the virus mutated and spread from one region to another.
-YN

